
Product of Conception Karyotyping by Cell-Free Fetal DNA Analysis
POCADAVANCE cfDNA Test is an advanced molecular test that, using groundbreaking technologies, determine the karyotype of product of conception (POC). By analyzing the circulating cell-free fetal DNA (cfDNA) in maternal blood, using the latest fully automated sequencing technologies (Next Generation Sequencing - NGS), it screens for genome-wide numerical and structural chromosomal abnormalities, providing unparalleled accuracy and detection compared to traditional karyotyping. POCADAVANCE cfDNA Test is able to provide information on the possible genetic causes of a spontaneous miscarriage, with the aim of helping the couple in family planning with specific reproductive genetic counseling.
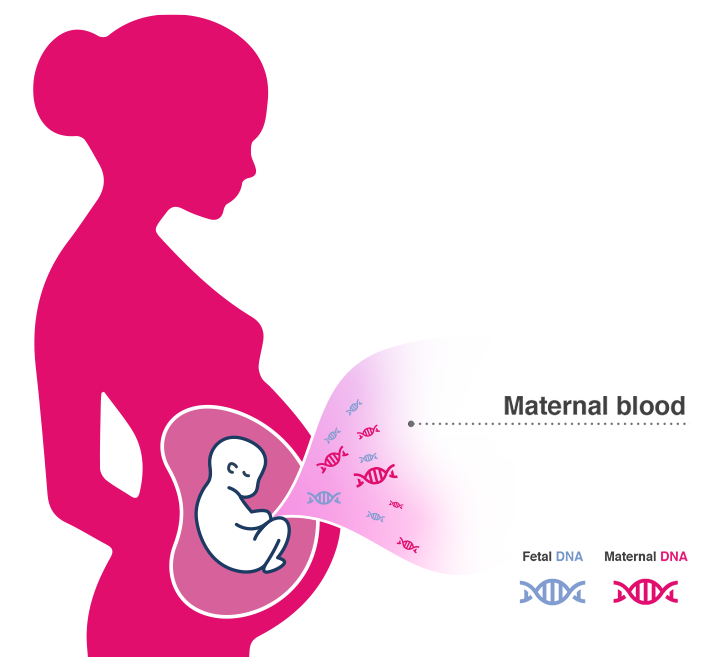
During pregnancy, placental trophoblasts, through a physiological process known as apoptosis, releases DNA fragments into the maternal blood, starting from the 5th week of gestation. This DNA is also named circulating cell-free fetal DNA (cfDNA). During miscarriage, the placental tissue continues to release cfDNA into the maternal bloodstream, making it possible to perform early non-invasive investigations, thus obtaining valuable information on the genetic causes of the abortion.
4 Yaron et al., 2020
5 Colley et al., 2020
6 Hartwig et al. 2023
A GROUNDBREAKING TECHNOLOGY THAT MAKES THE DIFFERENCE

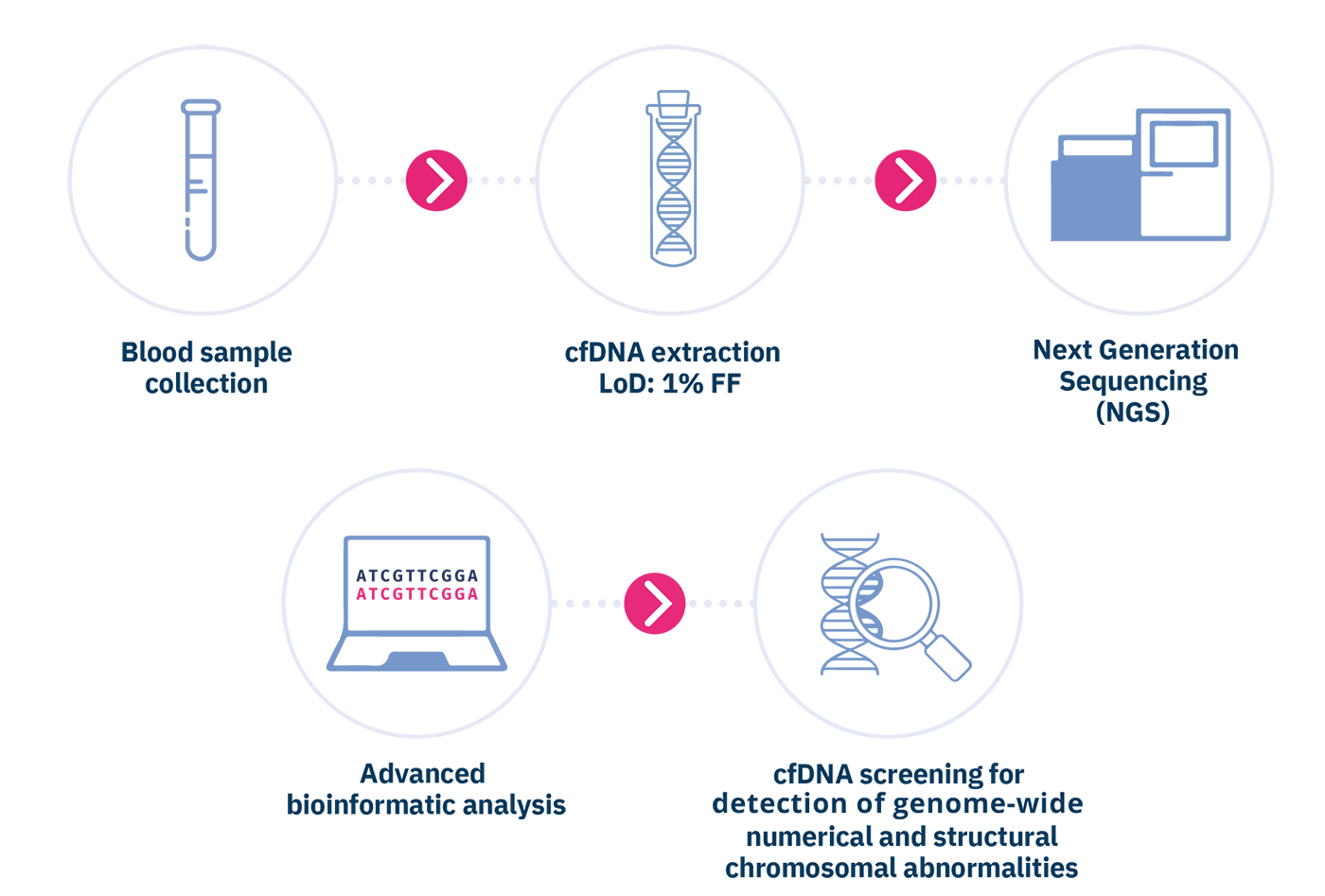
Circulating cell-free DNA is purified from the plasma component of anti-coagulated maternal whole blood sample. Subsequently, the cfDNA is analyzed by means of the innovative massive parallel sequencing (MPS) technology of the entire fetal genome, using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) sequencers. The chromosomal sequences are then quantified through an advanced bioinformatics analysis, in order to detect fetal chromosomal imbalances, identified by a greater amount of fetal sequences relating to a specific chromosome higher than a "normal". Blood draw must be performed immediately after confirming the miscarriage, and in any case before performing curetage, or within 24h from POC expulsion. The test can be performed in case of spontaneous abortions of single or twin pregnancies, monozygotic or dizygotic, with at least 5 weeks of gestation.
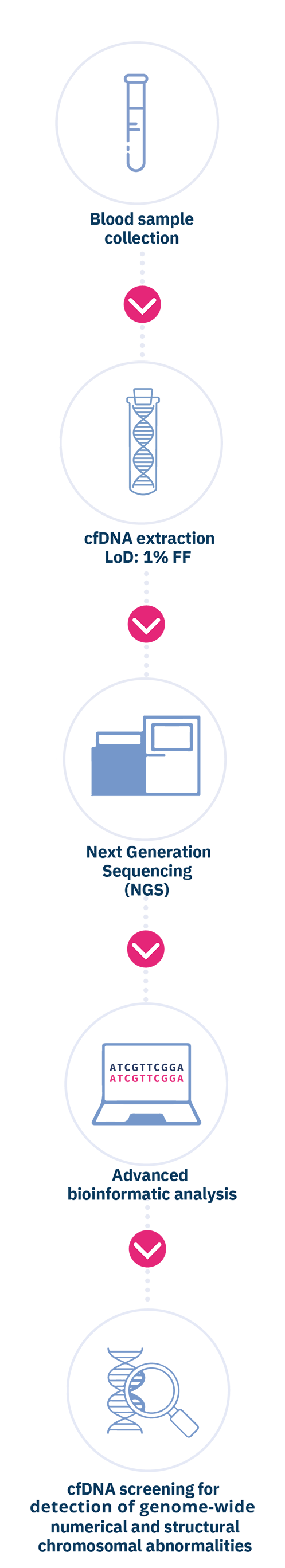
Circulating cell-free DNA is purified from the plasma component of anti-coagulated maternal whole blood sample. Subsequently, the cfDNA is analyzed by means of the innovative massive parallel sequencing (MPS) technology of the entire fetal genome, using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) sequencers. The chromosomal sequences are then quantified through an advanced bioinformatics analysis, in order to detect fetal chromosomal imbalances, identified by a greater amount of fetal sequences relating to a specific chromosome higher than a "normal". Blood draw must be performed immediately after confirming the miscarriage, and in any case before performing curetage, or within 24h from POC expulsion. The test can be performed in case of spontaneous abortions of single or twin pregnancies, monozygotic or dizygotic, with at least 5 weeks of gestation.
FETAL FRACTION AND LIMIT OF DETECTION



The fetal fraction (FF), i.e. the proportion of cfDNA in the maternal plasma that is of fetal origin, is a key determinant of assay performance and represents an important quality parameter of the test. If there is sufficient fetal cfDNA in the plasma sample, then the assay can provide accurate counting of the fetal chromosome fragments. The larger the FF, the better the ability to distinguish between euploid and aneuploid pregnancies, thereby the better the test performance. Instead, if the FF is too low, then a chromosomal abnormality could be masked by the overwhelming proportion of euploid maternal cfDNA, thereby increasing the risk of achieving false negative test results. The high resolution sequencing technology used to perform the POCADAVANCE cfDNA allows to reliably detect fetal chromosomal abnormalities at a FF down to 1%.
BENEFITS

 cfDNA testing
cfDNA testing
- Non-invasive test, performed by a simple blood sample collected from 5^ weeks of gestation;
- Test executable even in very early stages of abortion, before performing curetage.
 Cell culture is not required
Cell culture is not required
- Exclusion of the risk of achieving no results due to lack of cell growth;
- Significant reduction in turnaround time (3-5 days), instead of the 15-20 days required with “tradizional” karyotyping;
 High reliability of results
High reliability of results
- Exclusion of the risk deriving from the growth in culture of maternal cells instead of fetal ones;
- Quality derived from NGS-based molecular karyotyping.
 Greater resolution and accuracy compared to traditional karyotyping.
Greater resolution and accuracy compared to traditional karyotyping.
- Much higher resolution: 5 Mb instead of 10-15 Mb for the traditional karyotyping;
- Ability to precisely define, through a sophisticated bioinformatics analysis, the altered genomic region, and therefore also the genes it contains, allowing to predict the clinical consequences produced by the chromosomal abnormality found.


 Italiano
Italiano English
English